First-party data is a valuable asset for marketers in today's data-driven landscape. It refers to the information collected directly from customers or users by a company or organization. This data is obtained through various touch points such as website interactions, mobile app usage, customer surveys, or offline interactions.
It provides marketers with unique insights into their audience's behaviors, preferences, and interests, enabling them to personalize marketing campaigns and deliver more relevant and engaging experiences.
Statistics show the growing significance of first-party data in marketing strategies. According to a study conducted by Econsultancy, 82% of marketers consider first-party data crucial for their success.
Additionally, another research report by Advertiser Perceptions revealed that 92% of marketers believe that first-party data is the most valuable for driving marketing insights and decision-making.
These statistics highlight the importance of tracking and leveraging first-party data to enhance marketing effectiveness and drive better results.
What is First-Party Data
First-party data refers to the information that a company collects directly from its own customers or users. It is obtained through various channels such as websites, mobile apps, customer surveys, purchase histories, and interactions with the brand both online and offline.
This data is owned and controlled by the company, making it a valuable and reliable source of information.
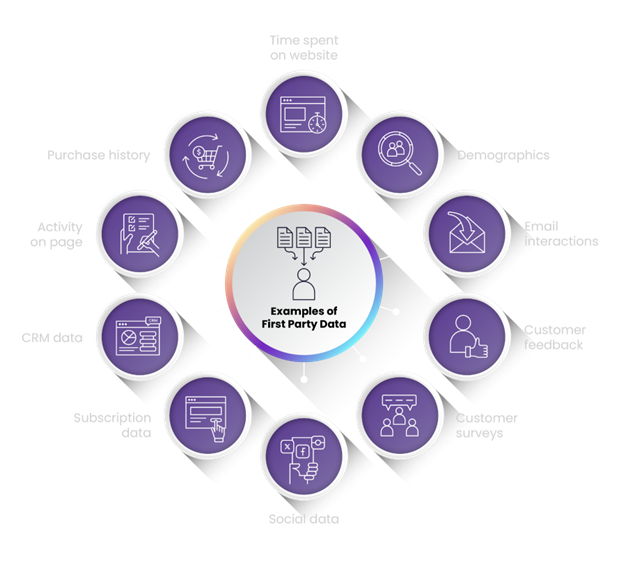
Examples of first-party data include:
- Website Data: Information gathered from website interactions, such as page views, clicks, time spent on site, and bounce rates.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Data: Data collected through customer interactions, transactions, and preferences stored in a CRM system.
- Email Marketing Data: Data obtained from email campaigns, including open rates, click-through rates, and user engagement.
- Social Media Data: Data derived from social media platforms, such as followers, likes, shares, and comments.
- Offline Interactions: Data collected from in-store purchases, loyalty programs, or customer service interactions.
Why is First-Party Data Important
It doesn’t Rely on Third-Party Data
First-party data is essential because it allows marketers to have direct control over the data they collect. Unlike third-party data, which is acquired from external sources, first-party data is obtained directly from the target audience.
This reduces reliance on external data providers, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and compliance with privacy regulations. By relying on their own data, marketers can have a deeper understanding of their customers and make data-driven decisions based on trusted information.
Higher Return on Investment
Utilizing first-party data can lead to a higher return on investment (ROI) for marketing efforts. Since first-party data provides insights into customers' behaviors, preferences, and interests, marketers can tailor their campaigns and messaging to be highly relevant and personalized.
This targeted approach increases the likelihood of engagement, conversion, and customer satisfaction, ultimately driving a higher ROI for marketing initiatives.
Empowers Consumers
First-party data empowers consumers by enabling brands to deliver more personalized and relevant experiences. By understanding customer preferences and interests, marketers can provide tailored recommendations, offers, and content that align with individual needs.
This not only enhances the customer experience but also fosters a sense of empowerment and satisfaction, as customers feel understood and valued by the brand.
Boosts Brand Loyalty
First-party data plays a vital role in building and strengthening brand loyalty. By leveraging customer insights, marketers can create personalized experiences and engagement strategies that resonate with their audience.
This leads to a deeper emotional connection between the customer and the brand, fostering loyalty, trust, and long-term relationships. Brands that effectively utilize first-party data can create personalized loyalty programs, targeted promotions, and customized communications that reinforce their value proposition and keep customers engaged and loyal.
Deeper Customer Insights
First-party data provides marketers with deeper insights into customer behaviors and preferences. By analyzing data collected directly from customers, marketers can uncover valuable patterns, trends, and segments within their audience. This knowledge helps in identifying new opportunities, refining marketing strategies, and optimizing campaigns for better results.
Understanding customer insights on a granular level allows marketers to tailor their messaging, product offerings, and overall brand experience to meet the specific needs and preferences of their customers.
How to Collect First-Party Data
Customer Relationship Management Platforms
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms are valuable tools for collecting first-party data. These platforms allow businesses to gather and store customer information such as contact details, purchase history, preferences, and interactions.
By integrating CRM systems with various touchpoints, such as websites, email marketing, and customer service, businesses can collect and centralize valuable first-party data. This data can then be used to personalize marketing campaigns, improve customer service, and enhance overall customer experiences.
If you're looking to leverage first-party data effectively, consider implementing a robust CRM platform to gather, manage, and utilize valuable customer information. Explore the range of CRM solutions available in the market and choose one that aligns with your business needs and goals.
Websites
Websites serve as a powerful channel for collecting first-party data. By implementing various data collection methods such as web forms, cookies, and user registrations, businesses can gather valuable information directly from website visitors.
This includes contact details, browsing behavior, product interests, and more. Additionally, website analytics tools provide insights into user interactions, traffic sources, and navigation patterns, further enriching the first-party data collection process.
In-store Sales
For businesses with brick-and-mortar locations, in-store sales provide an opportunity to collect valuable first-party data. By implementing point-of-sale systems or customer loyalty programs, businesses can gather information such as purchase history, customer preferences, and demographic data.
This data can help businesses understand their customers better, tailor their offerings, and create targeted marketing campaigns.
Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs are an effective way to collect first-party data while also fostering customer loyalty. By encouraging customers to sign up for loyalty programs, businesses can gather information such as contact details, preferences, purchase behavior, and demographics.
This data can be used to personalize offers, rewards, and communications, as well as gain insights into customer preferences and behaviors, ultimately strengthening the relationship between the business and its customers.
First-Party Data Marketing Use Cases
Improve Targeting Precision
First-party data enables marketers to improve targeting precision by understanding their customers' behaviors, preferences, and interests. By analyzing first-party data, marketers can create highly targeted audience segments and deliver personalized messages, offers, and recommendations.
This precision targeting helps in maximizing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, increasing conversion rates, and reducing wasted ad spend.
Advance Omnichannel Measurement
First-party data allows marketers to measure and analyze customer interactions across multiple channels and touchpoints. By integrating first-party data from various sources such as websites, mobile apps, email campaigns, and offline interactions, marketers can gain a holistic view of the customer journey.
This comprehensive understanding of customer behavior and engagement enables better measurement of marketing performance and optimization of omnichannel strategies.
Map the Customer Journey
First-party data plays a crucial role in mapping the customer journey. By tracking and analyzing customer interactions at different touchpoints, marketers can gain insights into the stages, preferences, and pain points of the customer journey.
This information helps in identifying opportunities for engagement, optimizing user experiences, and delivering relevant content or offers at each stage of the customer's path.
Close the Loop on Attribution
First-party data allows marketers to close the loop on attribution by directly connecting customer actions to marketing efforts. By tracking the customer journey and analyzing first-party data, marketers can attribute specific actions or conversions to their marketing campaigns.
This attribution data provides insights into the most effective channels, messages, and tactics, enabling marketers to optimize their strategies for better ROI.
Create a Single View of the Customer
First-party data helps in creating a unified and comprehensive view of the customer. By consolidating data from various sources, such as CRM systems, website interactions, and offline sales, marketers can build a single customer profile.
This profile includes demographic information, preferences, purchase history, and engagement data. Having a single view of the customer allows marketers to personalize experiences, tailor communications, and deliver consistent messaging across all touchpoints.
Increase Relevancy
First-party data allows marketers to deliver more relevant and personalized experiences to their customers. By leveraging insights from first-party data, marketers can tailor their messaging, content, and offers based on individual preferences and behaviors.
This relevancy leads to higher customer engagement, increased conversions, and improved customer satisfaction. Ultimately, utilizing first-party data helps in building stronger customer relationships and driving long-term loyalty.
First-Party Data Challenges
Lack of a Data Strategy
One of the challenges with first-party data is the lack of a comprehensive data strategy. Without a clear plan in place, businesses may struggle to collect, organize, and leverage their first-party data effectively.
A data strategy should outline the objectives, processes, and tools required to collect, analyze, and activate first-party data in a way that aligns with business goals. Developing a data strategy helps businesses overcome challenges related to data silos, data quality, and data governance.
Resolving Identity and Building Profiles
Another challenge with first-party data is resolving identity and building accurate customer profiles. As customers interact with businesses across multiple touchpoints, it can be difficult to connect and reconcile data from different sources. Resolving identity involves accurately matching customer data points to create a unified customer profile.
Building accurate customer profiles requires data integration, data cleansing, and data enrichment processes to ensure the data is reliable and up-to-date.
Integrating Data Across Platforms
Integrating first-party data across platforms is a complex challenge that many businesses face. First-party data may reside in various systems, such as CRM platforms, website analytics tools, email marketing platforms, and more.
Integrating this data and creating a centralized view can be challenging due to different data formats, data structures, and technical limitations. Achieving seamless integration of first-party data allows businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers and deliver consistent experiences across channels.
Taking Action in Real-Time
Real-time actionability is a challenge when it comes to leveraging first-party data effectively. Timeliness is crucial in utilizing first-party data to deliver personalized experiences or targeted marketing campaigns.
Businesses need to have the infrastructure, tools, and processes in place to collect, analyze, and activate data in real-time. This includes leveraging technologies such as customer data platforms (CDPs), marketing automation, and real-time analytics to enable rapid decision-making and personalized interactions with customers based on up-to-date data.
Other Types of Data
Second-Party Data
Second-party data refers to data that is obtained directly from a trusted partner or another company rather than being collected firsthand by the data user. It involves a mutually beneficial exchange of data between two organizations.
In this scenario, the data provider shares their data with another organization, which can leverage this information to enhance their marketing efforts and gain additional insights about their target audience.
Second-party data can provide valuable insights and complement the existing first-party data of a company, allowing for a broader understanding of customer behaviors, preferences, and interests.
Examples of second-party data partnerships include:
- E-commerce Retailer and Payment Processing Company: An e-commerce retailer partners with a payment processing company to gain access to transactional data, including purchase history, payment methods, and customer demographics. This data allows the retailer to understand customer preferences, identify cross-selling or upselling opportunities, and personalize product recommendations.
- Travel Website and Hotel Chain: A travel website collaborates with a hotel chain to exchange data related to bookings, travel dates, destinations, and customer preferences. By leveraging this second-party data, the travel website can offer personalized travel recommendations, targeted promotions, and tailored vacation packages to its customers.
- Online Media Publisher and Social Media Platform: An online media publisher forms a partnership with a social media platform to share data on user engagement, content preferences, and demographic information. This collaboration enables the publisher to optimize content distribution, improve audience targeting, and deliver more relevant and engaging articles or videos to its readers.
- Health and Fitness App and Wearable Device Manufacturer: A health and fitness app teams up with a wearable device manufacturer to exchange data on users' activity levels, biometrics, and fitness goals. By combining this second-party data, the app can provide personalized workout plans, track progress, and offer customized health insights to its users.
- Automotive Manufacturer and Insurance Provider: An automotive manufacturer collaborates with an insurance provider to share data on driving behaviors, vehicle diagnostics, and maintenance records. This data exchange enables the insurance company to offer usage-based insurance policies and personalized premium rates, while the manufacturer can gain insights into vehicle performance and customer satisfaction.
These examples demonstrate how second-party data partnerships can unlock valuable insights, enhance targeting capabilities, and improve the overall customer experience.
Third-Party Data
Third-party data refers to data that is collected and aggregated by external sources or data providers who are separate from the organization using the data. It is collected from various channels, such as websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, data brokers, and other sources.
Third-party data is often purchased or licensed by companies to augment their own first-party data, providing additional information about their target audience or market segments.
Examples of third-party data include:
- Demographic Data: Data providers collect and aggregate demographic information such as age, gender, income, education level, and household composition. This data can be used by marketers to better understand their target audience and tailor their messaging and targeting strategies accordingly.
- Behavioral Data: Third-party data providers gather information on users' online behaviors, including browsing history, search queries, content consumption, and interactions with ads. This data can be utilized to create more targeted advertising campaigns, improve personalization, and optimize customer journeys.
- Geolocation Data: Location-based data is collected from sources like mobile apps and GPS devices to provide insights into consumers' physical movements and preferences. Geolocation data can be used for location-based targeting, geo-targeted advertising, and analyzing foot traffic patterns.
- Interest and Intent Data: Third-party data providers track users' online activities and interests, including the websites they visit, the content they engage with, and the products they show interest in. This data can help marketers understand customer preferences, identify potential leads, and deliver relevant advertisements and offers.
- Purchase Data: Data brokers and retailers aggregate transactional data from various sources to create datasets that showcase consumer purchase behavior. This data can be valuable for market research, competitive analysis, and identifying trends and patterns in consumer buying habits.
Third-party data can be a valuable resource for businesses to gain insights into larger market trends, reach new audiences, and refine their targeting strategies. However, it's important to consider data quality, privacy regulations, and the trustworthiness of data sources when utilizing third-party data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, first-party data is a powerful asset for marketers, providing invaluable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and interactions. By leveraging first-party data, marketers can enhance targeting precision, improve customer experiences, and drive meaningful results.
Establishing a solid first-party data strategy is crucial for businesses to effectively collect, manage, and leverage this data to inform their marketing efforts. A comprehensive first-party data strategy involves utilizing customer relationship management platforms, optimizing website data collection methods, leveraging in-store sales data, and implementing loyalty programs.
By combining these approaches, businesses can create a holistic view of their customers, gain deeper insights, and deliver personalized experiences. Overall, prioritizing first-party data empowers marketers to make data-driven decisions, build stronger customer relationships, and drive business growth.
With the ever-increasing importance of data in the digital landscape, developing a robust first-party data strategy should be a cornerstone of any marketer's approach, enabling them to stay ahead of the competition and create impactful marketing campaigns.
FAQs on First-Party Data Marketing
What is the most accurate example of first-party data?
The most accurate example of first-party data is the data collected directly from customers or users of a company's products or services. This can include information provided voluntarily by customers through registrations, surveys, forms, or account profiles.
First-party data is obtained directly from the source, ensuring its accuracy and reliability since it is based on real interactions and preferences expressed by the customers themselves.
What are the pitfalls of first-party data?
While first-party data offers numerous benefits, there are also some pitfalls to be aware of:
- Limited Scale: First-party data is limited to the interactions and behaviors of a company's own customers or users. It may not provide a comprehensive view of the entire target audience or market, especially for businesses with a smaller customer base. This limited scale can restrict the depth and breadth of insights that can be derived from the data.
- Biased Perspective: First-party data is inherently biased towards existing customers or users. It may not capture the perspectives, behaviors, and preferences of potential customers who have not interacted with the company yet. Relying solely on first-party data may result in a narrow understanding of the larger market and hinder efforts to reach and engage new audiences.
- Data Quality Concerns: While first-party data is generally more accurate and reliable than third-party data, there can still be challenges related to data quality. Incomplete or inconsistent data, duplicate entries, and outdated information can impact the reliability and usefulness of the data. Ensuring data hygiene and implementing robust data governance practices are important to mitigate these concerns.
- Lack of Contextual Information: First-party data typically provides information on customer behaviors and interactions but may lack contextual details. Without understanding the broader context surrounding customer actions, such as external factors or intent, it may be challenging to derive meaningful insights or make accurate predictions solely based on first-party data.
- Privacy and Compliance Risks: Collecting and using first-party data comes with privacy and compliance considerations. Businesses need to adhere to data protection regulations, obtain proper consent from customers, and ensure secure storage and handling of the data. Failure to comply with privacy regulations can lead to legal and reputational risks.
To overcome these pitfalls, it is important for businesses to adopt a holistic approach to data, combining first-party data with other data sources, such as second-party or third-party data, to gain a more comprehensive view of their target audience. Additionally, employing robust data analytics and data validation processes can help mitigate potential biases and ensure data accuracy.
Can you use your 1st party data to target customers?
One of the best features of first-party data is how easily it transfers across your various social network profiles. Ads on Facebook may be directed to specific groups of people by uploading a list of email addresses. The same list may be uploaded to Google Ads to specifically target those individuals.
How can I improve my first-party data?
To improve your first-party data, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Enhanced Data Collection Methods: Optimize your data collection methods across various touchpoints. This can include improving website analytics, implementing robust forms and surveys, integrating customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and utilizing data capture tools to gather more comprehensive and accurate data directly from your customers.
- Data Enrichment and Validation: Regularly update and validate your first-party data to ensure its accuracy and relevance. Use data enrichment techniques to enhance your existing data with additional attributes or demographic information. This can help create more detailed customer profiles and improve targeting precision.
- Encourage Data Sharing and Consent: Obtain explicit consent from your customers to collect and use their data for marketing purposes. Implement transparent data sharing policies and clearly communicate the benefits of sharing data with your organization. Incentivize customers to provide accurate and complete information through loyalty programs, personalized offers, or exclusive access to content.
- Data Integration and Centralization: Integrate data from different sources, such as your website, CRM platform, social media channels, and offline interactions, to create a centralized view of your customers. This enables you to gain a holistic understanding of their behaviors and preferences, leading to more effective personalization and targeted marketing efforts.
- Data Governance and Compliance: Establish robust data governance practices to ensure data security, privacy, and compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. Implement procedures to handle data breaches, regularly audit data access and usage, and educate employees about data protection best practices.
- Invest in Analytics and Insights: Leverage data analytics tools and technologies to extract actionable insights from your first-party data. Use advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive modeling or segmentation, to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities within your customer data. This can help drive data-driven decision-making and optimize marketing strategies.
By implementing these strategies, you can enhance the quality, depth, and usability of your first-party data, leading to more effective customer targeting, improved personalization, and better overall marketing performance.




