Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics are essential tools for measuring business performance and driving growth. According to a survey conducted by Deloitte, 65% of businesses believe that their KPIs are effective in driving performance, and 63% use KPIs to align their business strategies.
On the other hand, metrics are used to measure specific data points that contribute to a business's overall performance. Metrics provide insights into how well a business is performing in a particular area, such as marketing, sales, or operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the differences between KPIs vs metrics and how they can be used to help businesses grow. We will also discuss the key characteristics of effective KPIs and metrics and provide examples of how they can be used to drive performance.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a clear understanding of how KPIs and metrics can be used to measure and improve business performance.
What is A KPI?
If you’re wondering what is a KPI, it is a metric used by organizations to measure their progress toward achieving their strategic goals. KPIs are quantifiable and specific, and they help businesses understand whether they are meeting their objectives.
The meaning of KPIs is to provide a way for organizations to track their performance over time and make data-driven decisions to improve their operations. KPI metrics can be used in various areas of a business, including finance, marketing, sales, and customer service.
Examples of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
There are numerous examples of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that businesses can use to measure their performance. The choice of KPIs will depend on the specific goals of the business and the area of operations being measured.
Here are some examples of KPIs in different areas:
Customer KPI
These KPIs focus on measuring customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. Examples of customer KPIs include Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), and Customer Churn Rate.
Operational KPI
These KPIs measure the efficiency and effectiveness of operational processes within a business. Examples of operational KPIs include Cycle Time, Lead Time, Production Efficiency, and On-time Delivery.
Marketing KPI
These KPIs measure the success of marketing campaigns and initiatives. Examples of marketing KPIs include Website Traffic, Conversion Rate, Cost per Acquisition (CPA), and Return on Investment (ROI).
Sales KPI
These KPIs measure the performance of the sales team and the effectiveness of the sales process. Examples of sales KPIs include Sales Growth, Sales Conversion Rate, Sales per Rep, and Sales per Customer.
Financial KPI
These KPIs measure the financial performance of a business, including revenue, profit, and cash flow. Examples of financial KPIs include Gross Profit Margin, Operating Profit Margin, Return on Investment (ROI), and Return on Assets (ROA).
What Are Metrics?
Metrics are numerical measurements that businesses use to track specific data points and assess performance in a particular area. Metrics provide businesses with insights into their operations and can help identify areas for improvement.
Key metrics are those that have the most significant impact on achieving business goals.
The meaning of metrics is to provide businesses with quantifiable data that can be used to evaluate performance. Examples of key metrics include website traffic, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost, and employee turnover rate.
By tracking these metrics over time, businesses can identify trends and patterns, make data-driven decisions, and optimize their operations for maximum efficiency and effectiveness. Overall, metrics play a vital role in helping businesses measure performance, identify opportunities for improvement, and drive growth.
Examples of Metrics
Metrics are quantitative measures that businesses use to track specific data points and assess performance. The choice of metrics depends on the business goals and the area of operations being measured. Here are some examples of metrics in different areas:
Customer metrics
These metrics focus on measuring customer behavior and engagement. Examples of customer metrics include Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), Customer Churn Rate, Customer Retention Rate, and Net Promoter Score (NPS).
Operational metrics
These metrics measure the efficiency and effectiveness of operational processes within a business. Examples of operational metrics include Cycle Time, Lead Time, On-time Delivery, and Production Efficiency.
Marketing metrics
These metrics measure the success of marketing campaigns and initiatives. Examples of marketing metrics include Website Traffic, Conversion Rate, Cost per Lead (CPL), and Return on Investment (ROI).
Sales metrics
These metrics measure the performance of the sales team and the effectiveness of the sales process. Examples of sales metrics include Sales Growth, Sales Conversion Rate, Sales per Rep, and Sales per Customer.
Financial metrics
These metrics measure the financial performance of a business, including revenue, profit, and cash flow. Examples of financial metrics include Gross Profit Margin, Operating Profit Margin, Return on Investment (ROI), and Return on Assets (ROA).
KPI vs. Metrics: Key Differences
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics are both important in measuring performance and making data-driven decisions, but there are some key differences between KPIs vs metrics.
| KPI | Metrics | |
|---|---|---|
| Track Data & Measure Goals | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are a type of metric that measures progress toward a specific goal or objective. KPIs are used to evaluate the success of a particular strategy or initiative. | Metrics are quantitative measurements that track specific data points such as page views, bounce rates, conversion rates, etc. Metrics are used to identify trends and patterns in data. |
| Fixed Timeframe Decision | KPIs are often used to evaluate long-term success and typically have a fixed timeframe, such as monthly or quarterly. | Metrics can be used for both short-term and long-term decision-making, as they provide ongoing, real-time data. |
| Focus Degree Level | KPIs tend to focus on higher-level objectives, such as overall revenue growth or customer satisfaction. | Metrics can focus on more granular details, such as the number of clicks on a particular page or the time spent on a specific website feature. |
| Revenue Targeted | KPIs are often revenue-targeted and help businesses monitor progress toward specific financial targets. | Metrics can provide insights into revenue generation but may also measure other non-revenue-related data points such as engagement, traffic, or user behavior. |
Why KPIs and Metrics are Important
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and metrics are essential tools for measuring the success of a business or project. They provide quantifiable measures of progress toward specific goals and enable businesses to track their performance over time.
By regularly monitoring KPIs and metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their operations.
KPIs and metrics are important because they provide a clear understanding of a business's performance in real-time. This information is critical for making strategic decisions, setting goals, and prioritizing actions.
KPIs and metrics also help businesses to identify trends and patterns in their performance data, which can be used to develop new strategies, improve processes, and capitalize on opportunities.
By measuring and tracking the right KPIs and metrics, businesses can stay competitive, drive growth, and achieve their objectives.
In addition, KPIs and metrics are important for measuring the return on investment (ROI) of business activities. By tracking the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, sales initiatives, and other investments, businesses can determine which activities are generating the best results.
This information can be used to optimize spending, reduce waste, and increase profits. Ultimately, KPIs and metrics help businesses to make data-driven decisions that improve their bottom line and drive long-term success.
How KPIs and Metrics Work Together
KPIs and metrics work together to help organizations achieve their goals. Metrics provide detailed information on specific areas of performance, while KPIs measure progress toward broader business objectives.
Metrics serve as the building blocks for KPIs, providing the necessary data to track progress toward a specific goal. For example, a company may track metrics such as website traffic and conversion rates to calculate its KPI of increasing online sales.
KPIs and metrics also work together to identify areas for improvement and guide decision-making. By analyzing metrics and KPIs, organizations can gain insights into their performance, identify trends and patterns, and make informed decisions about future strategies.
For example, a company may identify a low conversion rate on a specific webpage through metrics analysis. They can then set a KPI to improve that conversion rate and use metrics to track progress toward that goal.
Choosing the Right KPI and Metrics for Your Business
KPIs and metrics help to identify areas that require improvement, monitor progress, and evaluate the effectiveness of strategies.
KPIs should align with goals
KPIs should align with the organization's goals to ensure that all efforts and resources are directed towards achieving those objectives. This alignment helps to ensure that the organization is focused on the metrics that matter the most and that all activities are working towards achieving the desired outcomes.
Choosing the right metrics for KPIs
It’s important to choose the right metric for KPIs as it ensures that the chosen KPIs are being measured most accurately and efficiently. Businesses must select relevant, timely, and reliable metrics to obtain accurate insights into their performance.
Measurable KPIs required
Measurable KPIs are necessary for a business to evaluate the effectiveness of its strategies and measure its progress over time. Non-measurable KPIs can be challenging to track and quantify progress accurately.
Ensure the accuracy of KPIs and metrics
It is essential to ensure the accuracy of KPIs and metrics to ensure that the data used to evaluate the business's performance is valid and reliable. This accuracy is necessary to make informed decisions based on the insights obtained from the data.
Avoid vanity metrics
Businesses must avoid vanity metrics as they can be misleading and do not provide meaningful insights into the organization's performance. Vanity metrics focus on the superficial aspects of the business and do not provide any value in terms of the business's objectives and goals.
Changing KPIs over time
It may be necessary to change KPIs over time as the business evolves and goals change. It is essential to be flexible in adapting to changing circumstances and adjusting KPIs accordingly to ensure that the business is always aligned with its objectives.
Track Your Business Growth with Comprehensive Metrics
Tracking metrics is essential for businesses to measure their progress and ensure sustainable growth. With the help of KPI tracking and metric dashboard, companies can monitor their performance and identify areas that need improvement.
By regularly checking these metrics, businesses can evaluate their strategies and make informed decisions to optimize their operations.
Audit Business Health
One of the key benefits of tracking metrics is the ability to audit business health. By measuring KPIs and other relevant metrics, companies can assess their financial stability, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
These insights provide valuable information to identify areas of strengths and weaknesses and allow businesses to focus their efforts on areas that require attention.
Track progress using the dashboard
Tracking progress using the dashboard allows businesses to gain a comprehensive view of their performance, making it easier to identify trends and patterns. By analyzing data and drawing insights, companies can make data-driven decisions that are aligned with their goals.
The dashboard presents KPIs and metrics in an easily understandable format, allowing businesses to monitor their performance and make adjustments accordingly.
Check out Arena’s metrics dashboard as it offers a plethora of information in an easy-to-understand and-track manner:
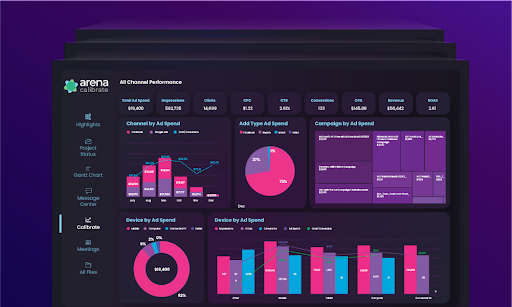
Make necessary adjustments
By regularly tracking metrics, businesses can make necessary adjustments to their operations. These metrics provide a clear understanding of what is working and what is not, allowing companies to adapt quickly to changing circumstances.
This approach ensures that businesses can optimize their operations and stay ahead of the competition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between KPIs and metrics is essential for measuring and improving business performance. While both KPIs and metrics are important, KPIs are more strategic and focused on achieving specific business objectives, while metrics are more operational and provide detailed insights into performance.
Choosing the right KPIs and metrics is crucial for success, and they should be aligned with business goals and regularly audited to ensure accuracy. By tracking metrics and dashboard tools, businesses can monitor progress, make necessary adjustments, and drive growth.
FAQ on KPI vs. Metrics
How do KPIs and metrics help me make data-driven decisions for my business?
KPIs and metrics are essential tools for making data-driven decisions in any business. They allow you to track your progress towards specific goals and objectives, providing insight into areas where you may need to improve or adjust your strategies.
By monitoring KPIs and metrics, you can identify patterns and trends in your data, making it easier to recognize what is working and what isn't.
KPIs should be chosen carefully, ensuring that they align with your business goals and clearly indicate progress toward those goals. Conversely, metrics provide specific data points that help you measure progress toward your KPIs.
When working together, KPIs and metrics comprehensively view your business performance.
By regularly tracking KPIs and metrics, you can audit the health of your business, track progress using a dashboard, and make necessary adjustments to your strategies. This helps you identify opportunities for growth and respond to challenges quickly, ultimately driving business success.
How do KPIs and metrics help me communicate the value of my business to stakeholders?
KPIs and metrics provide a clear and concise way to communicate the value of your business to stakeholders. By tracking and measuring important data points, you can show the progress and success of your business over time.
For example, you can use KPIs to show how your business is meeting key objectives, such as increasing revenue or improving customer satisfaction. Metrics can provide more granular details on how these objectives are being achieved, such as the number of new customers acquired or the average time spent on your website.
By presenting this data in an easy-to-understand format, such as a dashboard or report, stakeholders can quickly see the value your business is providing and its impact. This can be especially important when communicating with investors, board members, or other key decision-makers who must clearly understand your business's performance.
In addition, KPIs and metrics can also help identify areas of improvement and opportunities for growth, which can further demonstrate the value of your business to stakeholders. Overall, KPIs and metrics can help you communicate the value of your business in a tangible and data-driven way.
How can I track and measure the impact of my business efforts on revenue and profitability?
To track and measure the impact of your business efforts on revenue and profitability, you need to identify the relevant KPIs and metrics and establish a system for monitoring and analyzing them. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Define your revenue and profitability goals: Identify your desired revenue and profit targets and the timeline for achieving them.
- Identify relevant KPIs and metrics: Select KPIs and metrics that align with your revenue and profit goals, such as conversion rate, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and gross profit margin.
- Establish a system for tracking and analyzing data: Utilize a web analytics tool or a business intelligence platform to collect and analyze data on your selected KPIs and metrics.
- Regularly monitor and evaluate performance: Review your data on a regular basis to track progress towards your revenue and profit goals. Use this information to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to your business strategies.
By tracking and measuring the impact of your business efforts on revenue and profitability, you can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of your business strategies and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and success.
What are some common metrics for measuring business operations?
There are several common metrics used for measuring business operations. Here are some examples:
- Revenue: The total amount of money earned from sales of products or services.
- Gross profit margin: The percentage of revenue that is left after accounting for the cost of goods sold.
- Net profit margin: The percentage of revenue that is left after accounting for all expenses, including overhead costs.
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer, calculated by dividing total marketing and sales costs by the number of new customers acquired.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): The estimated value of a customer over the entire duration of their relationship with the business.
- Churn rate: The rate at which customers stop doing business with the company over a certain period of time.
- Inventory turnover: The number of times inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period of time.
- Website traffic: The number of visitors to a company's website over a specific period of time.
- Conversion rate: The percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
- Employee turnover rate: The percentage of employees who leave the company over a specific period of time.
Can KPIs and metrics be used interchangeably in a business context?
KPIs and metrics cannot be used interchangeably in a business context. While both are used to measure business performance, KPIs are specific, strategic, and measurable indicators that are critical to achieving business objectives.
In contrast, metrics are more general measurements that provide insights into various aspects of business performance.
KPIs are used to track progress toward achieving business goals and objectives, while metrics provide context and support decision-making. It is important to distinguish between the two and use them appropriately to measure and improve business performance effectively.




