In today's digital age, businesses have access to vast amounts of customer data, ranging from demographic information to browsing behavior and purchase history. Harnessing this data effectively is crucial for marketers to drive targeted campaigns, personalized experiences, and ultimately, achieve business growth.
This is where Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) come into play. A CDP is a powerful tool that allows marketers to consolidate, analyze, and utilize customer data from various sources in a unified platform. In this article, we will explore the advantages of using Customer Data Platforms and provide guidelines for marketers to make the most out of this innovative technology. Here are some statistics that display the importance of CDPs:
- According to a survey by Winterberry Group, the CDP market is expected to reach $1 billion in revenue by 2024.
- According to a report by Ascend2, 64% of marketers consider improving customer segmentation and targeting as the top benefit of implementing a CDP.
- In a survey conducted by the CDP Institute, 68% of respondents stated that CDPs help improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The CDP market is rapidly growing, with more than 50% of organizations planning to invest in a CDP solution in the next two years, as per a report by the CMO Council.
In this article, we’ll offer a comprehensive understanding of customer data platforms (CDP), including how they work, benefits, and best practices.
What is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a software platform that enables businesses to collect, organize, and analyze customer data from various sources. It serves as a centralized hub for customer information, allowing marketers to gain a comprehensive view of their customers and create personalized experiences.
CDPs gather data from multiple touchpoints such as websites, mobile apps, CRM systems, email campaigns, and more, and unify it into a single, actionable profile for each customer. By leveraging this consolidated data, marketers can better understand customer behavior, preferences, and needs, enabling them to deliver targeted marketing campaigns, optimize customer journeys, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
These platforms provide a powerful solution for businesses to leverage their customer data effectively and drive meaningful interactions with their audience.
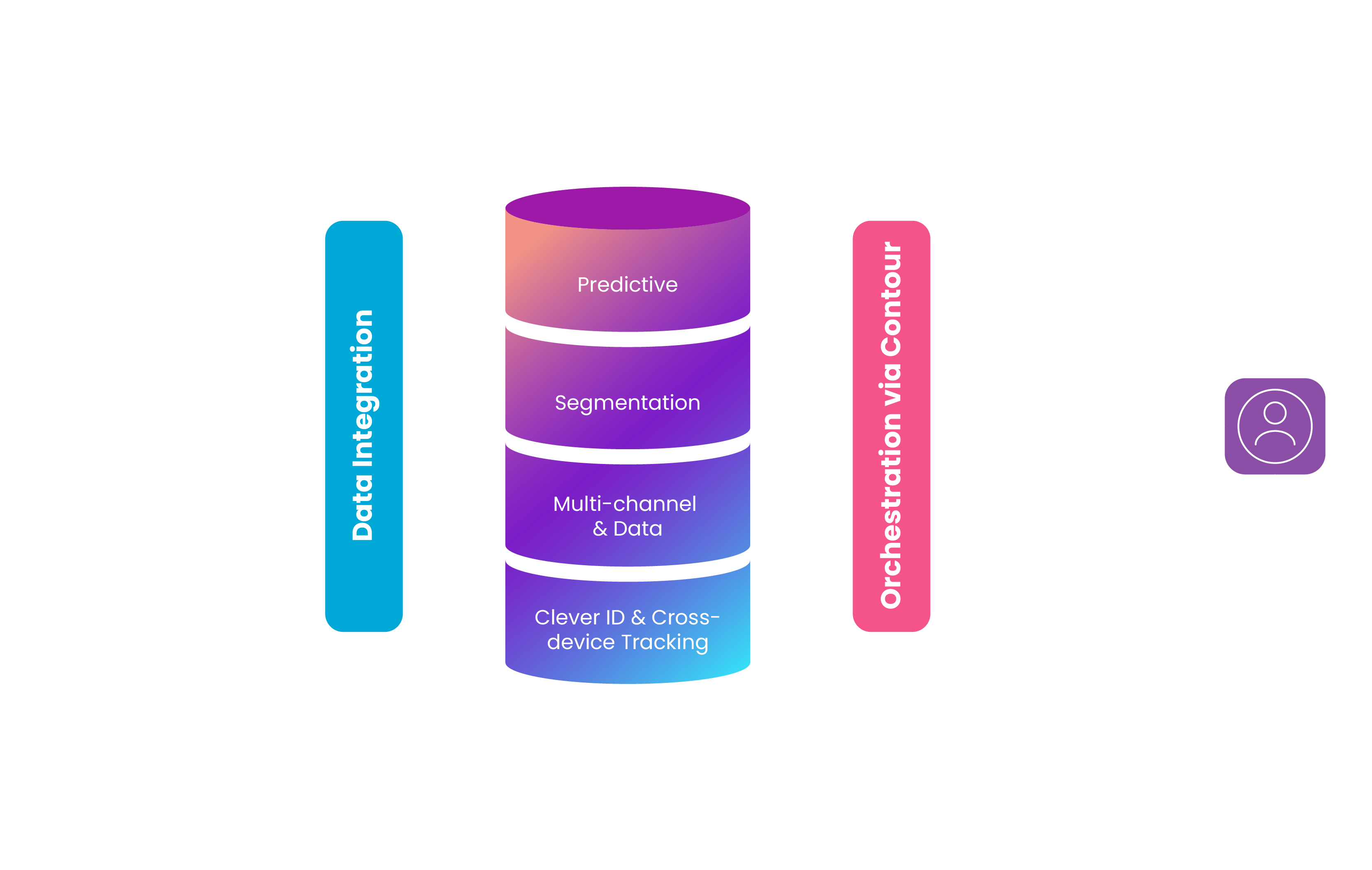
Benefits of a Customer Data Platform
Here are some of the most important benefits of a customer data platform:
Enhanced Collaboration within the Enterprise
A Customer Data Platform facilitates better collaboration within an organization by providing a centralized data repository accessible to various teams. Marketing, sales, and customer service teams can work together, leveraging the same customer data to align their strategies and deliver a unified customer experience.
This collaboration leads to improved cross-functional communication, streamlined processes, and ultimately, better business outcomes.
Efficient Management of Customer Data
A CDP enables efficient management of customer data by consolidating information from multiple sources into a single, unified view. It eliminates data silos and ensures data accuracy and consistency. With a CDP, businesses can efficiently organize, cleanse, and validate customer data, making it readily available for analysis and decision-making.
This streamlined management of customer data enhances operational efficiency, reduces manual errors, and enables faster access to actionable insights.
Seamless Integration of Systems
A Customer Data Platform seamlessly integrates with various systems and data sources, including CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, email marketing tools, and more. It harmonizes data from these disparate sources, creating a unified customer profile.
This integration eliminates data fragmentation and enables real-time data syncing, ensuring that all customer touchpoints are up-to-date and synchronized. As a result, marketers can deliver consistent and personalized experiences across channels, driving customer engagement and loyalty.
Optimized Marketing Processes
A CDP empowers marketers with advanced segmentation and targeting capabilities. By leveraging comprehensive customer profiles and behavioral data, marketers can create highly targeted campaigns tailored to specific audience segments.
This optimization of marketing processes enables marketers to deliver personalized content, offers, and recommendations to customers, increasing engagement and conversion rates. Additionally, marketers can automate workflows, personalize customer journeys, and measure campaign effectiveness, leading to improved marketing ROI.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns for businesses. A Customer Data Platform provides robust security measures to safeguard customer data. It ensures compliance with data protection regulations and employs encryption, access controls, and auditing mechanisms to protect sensitive information.
By implementing a CDP, businesses can enhance data security, build customer trust, and mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
Robust Regulatory Compliance
Customer Data Platforms are designed to adhere to regulatory requirements, such as GDPR and CCPA, ensuring businesses comply with data privacy laws. CDPs enable data governance practices, allowing businesses to track and document data usage, consent management, and data subject requests.
With a CDP, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to data compliance and avoid potential legal and reputational risks.
Alternative to Third-Party Cookies
With the phasing out of third-party cookies by major browsers, businesses are seeking alternative methods to collect and leverage customer data. A Customer Data Platform offers a first-party data solution, enabling businesses to gather and utilize their own customer data effectively.
CDPs allow for tracking and analyzing customer interactions across owned channels, providing valuable insights for personalized marketing strategies, without relying heavily on third-party cookies.
Deeper Customer Insights through Analytics
A Customer Data Platform integrates with analytics tools, enabling businesses to derive deeper insights from customer data. Marketers can leverage advanced analytics capabilities to identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data, uncovering valuable insights about customer behavior, preferences, and engagement.
These insights drive data-driven decision-making, helping marketers optimize their strategies, improve customer experiences, and identify new business opportunities.
Best Practices for Customer Data Platform Adoption
If you want to effectively implement a customer data platform, check out these top CDP best practices:
Identifying Key Business Objectives for CDP Implementation
Before adopting a Customer Data Platform, it is crucial to identify and align the key business objectives that the CDP will help achieve. Whether it's improving customer segmentation, enhancing personalization, or optimizing marketing campaigns, having clear objectives ensures that the CDP implementation is focused and aligned with business goals.
Establishing a Comprehensive Data Governance Framework
A robust data governance framework is essential for successful CDP adoption. This framework should define data ownership, access controls, data quality standards, and compliance protocols. By establishing clear guidelines and processes for data management, businesses can ensure the accuracy, integrity, and security of customer data within the CDP.
Selecting the Right CDP Technology
Choosing the appropriate CDP technology that aligns with your business requirements is crucial. Consider factors such as scalability, integration capabilities, customization options, and vendor support. Thoroughly evaluate different CDP solutions and select the one that best fits your organization's needs and can seamlessly integrate with existing systems and data sources.
Training Employees on CDP Usage
Proper training and education are essential for employees who will be working with the CDP. Provide comprehensive training on using the CDP interface, understanding data insights, and leveraging the platform's features effectively. This empowers employees to make the most out of the CDP, driving better decision-making and maximizing its potential.
Implementing an Effective Data Retention Policy
Establish a data retention policy that outlines how long customer data will be stored within the CDP. Consider legal and compliance requirements, as well as the need for historical data analysis. Implementing an effective data retention policy ensures that the CDP maintains relevant and up-to-date customer information, minimizing data clutter and optimizing system performance.
Utilizing Data Analysis Tools to Enhance Operations
Leverage data analysis tools and capabilities within the CDP to extract meaningful insights. Use data visualization, reporting, and predictive analytics to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement. By leveraging data analysis, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize operations, and deliver targeted experiences to customers.
Enhancing Customer Engagement with CDPs
Leverage the power of the CDP to enhance customer engagement by delivering personalized and relevant experiences. Utilize the unified customer profiles and behavioral data to segment customers, create tailored messaging, and deliver targeted campaigns across channels. By leveraging the CDP's capabilities, businesses can build stronger relationships with their customers and drive loyalty.
Planning and Implementing Clean Data Feeds
Ensure that data feeds into the CDP are clean, accurate, and well-structured. Plan and implement data cleansing and validation processes to eliminate duplicates, standardize data formats, and enhance data quality. This ensures that the data within the CDP is reliable, enabling accurate analysis and actionable insights.
Optimizing for Real-Time Results
Leverage the real-time capabilities of the CDP to drive immediate and relevant interactions with customers. Implement real-time data syncing, event triggering, and personalized messaging to deliver timely and contextually appropriate experiences. By optimizing for real-time results, businesses can stay agile, respond to customer needs promptly, and create impactful customer interactions.
Measuring the Success of Your CDP Implementation
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your CDP implementation. Monitor metrics such as customer engagement, conversion rates, customer lifetime value, and return on investment (ROI).
Regularly evaluate these metrics to assess the effectiveness of the CDP and make adjustments as needed to maximize its impact on business outcomes.
How to Choose an Ideal Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
Data sources
When selecting a CDP, consider the ability of the platform to integrate with and gather data from various sources. Ensure that the CDP can effectively collect data from sources such as websites, mobile apps, CRM systems, email marketing tools, and more.
The CDP should support a wide range of data types and formats to ensure comprehensive data consolidation and analysis.
Privacy
Privacy is a crucial aspect to consider when choosing a CDP. Ensure that the platform adheres to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, and provides robust privacy features. Look for features like consent management, data anonymization, and the ability to handle customer data rights and preferences.
Prioritize a CDP that puts privacy and data protection at the forefront to maintain customer trust and compliance.
Security features
Data security is of utmost importance when selecting a CDP. Evaluate the security features provided by the platform, such as data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. The CDP should have measures in place to protect customer data from unauthorized access, breaches, and vulnerabilities.
Consider the platform's track record, certifications, and security protocols to ensure the highest level of data security.
Integration with other tools
Consider the compatibility and integration capabilities of the CDP with other tools and systems in your marketing technology stack. The CDP should seamlessly integrate with your existing CRM, marketing automation, analytics, and campaign management tools. This integration enables smooth data flow between systems, eliminates data silos, and facilitates a unified view of customer information across the organization.
Scalability
Assess the scalability of the CDP to accommodate your growing data needs. As your customer base expands and data volumes increase, the CDP should be able to handle the scale without compromising performance.
Look for a CDP that can efficiently process and analyze large volumes of data, scale resources as needed, and support future growth without sacrificing functionality or speed.
Cost
Consider the cost implications of implementing a CDP. Evaluate the pricing structure, including upfront costs, licensing fees, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Assess the value the CDP brings to your organization and weigh it against the cost.
Look for a CDP that aligns with your budget and provides a balance between affordability and the required features and capabilities. Consider factors like implementation costs, training, support, and any additional fees associated with data storage or usage.
By considering these factors, businesses can make an informed decision when choosing a Customer Data Platform that best fits their specific needs, ensuring effective data management, privacy compliance, security, integration capabilities, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Mistakes to Avoid when Implementing a Customer Data Platform
Here are some mistakes you should avoid while implementing a customer data platform:
- Lack of clear objectives: Failing to define specific business objectives for implementing a CDP can lead to a lack of focus and ineffective use of the platform.
- Poor data quality and governance: Neglecting data quality standards and failing to establish a comprehensive data governance framework can result in inaccurate and unreliable customer data within the CDP.
- Insufficient training and adoption: Inadequate training for employees on how to effectively use the CDP can limit its potential and hinder successful implementation across the organization.
- Overlooking data privacy and compliance: Ignoring data privacy regulations and failing to prioritize privacy features within the CDP can result in legal and reputational risks.
- Lack of integration with existing systems: Not considering the integration capabilities of the CDP with other tools and systems can lead to data silos and hinder a unified view of customer information.
- Poor scalability planning: Failing to anticipate future data growth and scalability requirements can result in performance issues and limitations as the business expands.
- Ignoring ongoing maintenance and support: Neglecting the need for regular maintenance, updates, and technical support can hinder the optimal performance and utilization of the CDP.
- Lack of measurement and optimization: Failing to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and regularly measure the success of the CDP implementation can hinder ongoing improvements and impact business outcomes.
- Overlooking change management: Not effectively managing organizational change and resistance to new processes and technologies can impede the adoption and success of the CDP.
- Underestimating implementation complexity: Underestimating the time, effort, and resources required for a successful CDP implementation can lead to delays and suboptimal outcomes.
Arena Calibrate: Best Customer Data Platform on the Market
Arena Calibrate is the leading CDP software that revolutionizes the way businesses manage and leverage their customer data. With its advanced capabilities and intuitive interface, it empowers organizations to gain valuable insights, optimize marketing strategies, and drive exceptional customer experiences.
Arena Calibrate takes the complexity out of data management, offering a comprehensive solution that ensures data accuracy, integration, and activation, making it the ultimate choice for businesses looking to unlock the full potential of their customer data.
Features
- Seamless data integration from multiple sources
- Robust data cleansing and enrichment capabilities
- Advanced segmentation and audience management
- Real-time customer data analytics and reporting
- Personalized marketing automation and campaign management
- Cross-channel data activation for targeted messaging
- GDPR and data privacy compliance tools
- Scalable and flexible architecture for growing businesses
Benefits
- Enhanced customer understanding for more personalized experiences
- Improved campaign performance and ROI
- Increased customer retention and loyalty
- Streamlined data workflows and reduced manual effort
- Faster time to market with real-time insights
- Optimized marketing strategies based on data-driven decisions
- Strengthened data security and compliance measures
- Future-proof solution adaptable to evolving business needs
Conclusion
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) offer numerous advantages for marketers, providing a centralized hub to collect, organize, and analyze customer data from various sources.
By adopting CDPs, businesses can enhance collaboration, efficiently manage customer data, seamlessly integrate systems, optimize marketing processes, ensure data security and privacy, comply with regulations, and gain deeper customer insights through analytics.
Leveraging the power of CDPs, marketers can easily analyze customer data, uncover valuable insights, and deliver personalized experiences that drive customer engagement and business growth.
Embracing these tools empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions and stay competitive in today's customer-centric landscape.
FAQ on Customer Data Platforms
How do Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) Differ from DMPs and CRMs?
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs), Data Management Platforms (DMPs), and Customer Relationship Management (CRMs) systems serve distinct purposes in managing and utilizing customer data. Here's how they differ:
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs):
- Focus: CDPs are designed to collect, consolidate, and unify customer data from various sources into a single, comprehensive customer profile. They prioritize creating a unified view of the customer across channels and touchpoints.
- Data Types: CDPs typically handle both identifiable and anonymous customer data, including first-party data collected directly from interactions with the business.
- Functionality: CDPs offer advanced data analytics and segmentation capabilities to derive actionable insights and deliver personalized experiences. They enable data activation across marketing and customer engagement channels.
- Use Cases: CDPs are primarily used for marketing purposes, supporting targeted campaigns, personalization efforts, and customer journey optimization.
Data Management Platforms (DMPs):
- Focus: DMPs primarily focus on aggregating and managing large volumes of anonymous, third-party data from various sources, such as cookies, ad impressions, and audience data purchased from data providers.
- Data Types: DMPs mainly handle anonymous data, often related to online behavior and audience segments.
- Functionality: DMPs specialize in audience segmentation, data analysis, and audience activation for advertising and media buying purposes. They provide insights into audience demographics, interests, and behavior patterns to optimize ad targeting.
- Use Cases: DMPs are primarily used by advertisers, publishers, and media agencies to improve ad targeting and campaign effectiveness.
Customer Relationship Management (CRMs):
- Focus: CRMs primarily focus on managing and nurturing customer relationships. They provide a central repository for customer data, interactions, and transactional history, helping businesses track and manage customer relationships and sales processes.
- Data Types: CRMs handle both identifiable and transactional data, often obtained through direct customer interactions and sales transactions.
- Functionality: CRMs offer features such as contact management, lead tracking, sales pipeline management, and customer service ticketing. They focus on improving customer engagement, sales, and service delivery.
- Use Cases: CRMs are widely used across sales, marketing, and customer service teams to manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and provide personalized customer experiences.
While there may be some overlap in functionality, each platform serves a distinct purpose in managing and leveraging customer data within different contexts and business objectives.
Can the CDP ingest data from various sources?
Yes, Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are designed to ingest data from various sources. One of the key features of CDPs is their ability to collect and consolidate customer data from multiple channels and touchpoints.
CDPs can ingest data from sources such as websites, mobile apps, CRM systems, email marketing tools, point-of-sale systems, social media platforms, and more. These platforms provide the infrastructure to aggregate data from both online and offline sources, allowing businesses to create a comprehensive and unified view of their customers.
By ingesting data from diverse sources, CDPs enable marketers to gain a holistic understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and interactions, leading to more targeted and personalized marketing efforts.
What are some potential future developments in CDPs?
Some potential future developments in Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) may include:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: CDPs could leverage advanced AI and machine learning algorithms to provide automated customer insights, predictive analytics, and personalized recommendations. These technologies can enhance data analysis capabilities and enable real-time decision-making.
- Voice and IoT Data Integration: As voice assistants and Internet of Things (IoT) devices become more prevalent, CDPs may evolve to include data integration from these sources. This would enable businesses to gather and analyze data from voice interactions, smart devices, and sensors, providing a more comprehensive understanding of customer behavior.
- Enhanced Privacy and Data Governance Features: With increasing concerns about data privacy, CDPs may focus on providing enhanced privacy and data governance features. This could include features such as enhanced consent management, data anonymization techniques, and tools for managing data subject rights and compliance with evolving privacy regulations.
- Cross-Channel Orchestration: CDPs could evolve to become more sophisticated in orchestrating customer experiences across multiple channels and touchpoints. This would involve real-time personalization and seamless integration with marketing automation and campaign management tools, allowing businesses to deliver consistent and personalized messaging to customers.
- Advanced Customer Segmentation: CDPs may develop more advanced customer segmentation capabilities, incorporating additional data points, predictive analytics, and behavioral insights. This would enable marketers to create highly targeted and granular customer segments for more effective marketing campaigns.
- Data Monetization: CDPs may offer opportunities for data monetization, allowing businesses to leverage their customer data by securely sharing or selling anonymized and aggregated insights to trusted partners or third-party data marketplaces.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: CDPs may integrate with emerging technologies such as blockchain, edge computing, and augmented reality (AR)/virtual reality (VR). These integrations could enhance data security, data processing speed, and customer experiences, respectively.
It's important to note that the future development of CDPs will depend on industry trends, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations. These potential developments can shape the evolution of CDPs as they continue to play a crucial role in managing and leveraging customer data for businesses.
What are some of the challenges of implementing a CDP?
Implementing a Customer Data Platform (CDP) can come with certain challenges. Some of the common challenges include:
- Data Integration Complexity: Integrating data from various sources into a CDP can be complex and time-consuming. Different data formats, systems, and data quality issues may arise, requiring careful mapping, transformation, and cleansing of data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Data Quality and Governance: Ensuring data quality and establishing a robust data governance framework can be challenging. Inaccurate or incomplete data can affect the overall effectiveness of the CDP and hinder data-driven decision-making. Maintaining data hygiene, addressing data duplication, and establishing data governance policies are crucial tasks.
- Organizational Alignment: Implementing a CDP often requires cross-functional collaboration and alignment within the organization. Different teams, such as marketing, IT, data, and customer service, may have different requirements and priorities, making it necessary to overcome silos and establish shared objectives.
- Resource and Expertise Requirements: Successfully implementing a CDP may require adequate resources, both in terms of budget and skilled personnel. Organizations need to allocate resources for technology infrastructure, data management, integration, training, and ongoing maintenance and support.
- Change Management: Introducing a CDP involves changes to existing processes and workflows. Employees may need to adapt to new tools, methodologies, and ways of working. Effective change management strategies, communication, and training are crucial to ensure smooth adoption and utilization of the CDP across the organization.
- Privacy and Compliance Considerations: With increasing data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws such as GDPR or CCPA can be a challenge. Implementing privacy features, obtaining proper consents, and handling data subject rights in the context of a CDP require careful attention to privacy and compliance requirements.
- Scalability and Performance: As the volume and complexity of data grow, scalability and performance become critical. CDPs need to handle increasing data volumes, provide real-time or near real-time capabilities, and scale their infrastructure to meet evolving business needs.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, ongoing monitoring and optimization, and a clear understanding of organizational objectives. With proper strategies in place, organizations can successfully navigate these challenges and harness the full potential of a CDP to drive better customer experiences and business outcomes.
How does a business measure the success of a CDP?
Measuring the success of a Customer Data Platform (CDP) implementation involves assessing various key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with business objectives. Here are some common metrics that businesses can use to measure the success of a CDP:
- Customer Engagement: Measure the impact of the CDP on customer engagement metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, time spent on site, repeat purchases, or customer loyalty and satisfaction scores. This indicates whether the CDP is effectively driving customer interactions and fostering deeper engagement.
- Personalization Effectiveness: Evaluate the success of personalization efforts driven by the CDP. Metrics such as click-through rates on personalized recommendations, uplift in conversion rates from personalized campaigns, or customer feedback on personalized experiences can indicate the effectiveness of the CDP in delivering relevant and tailored messaging.
- Marketing Campaign Performance: Analyze the performance of marketing campaigns powered by the CDP. Assess metrics like campaign reach, response rates, conversion rates, return on investment (ROI), or cost per acquisition (CPA) to determine how the CDP contributes to campaign effectiveness and marketing efficiency.
- Data Quality and Accuracy: Monitor the quality and accuracy of customer data within the CDP. Track metrics such as data completeness, data duplication rates, data validation errors, or data enrichment levels. Higher data quality and accuracy indicate that the CDP is successfully managing and maintaining reliable customer data.
- Operational Efficiency: Assess the impact of the CDP on operational efficiency. Look at metrics like data processing time, campaign execution time, or time-to-insights to measure improvements in data processing speed, campaign deployment, and the time it takes to derive actionable insights from customer data.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Evaluate the financial impact of the CDP by comparing the costs associated with implementing and maintaining the CDP with the value generated. This can include revenue growth, cost savings from improved targeting and personalization, or increased customer lifetime value.
- Customer Satisfaction: Gather customer feedback, conduct surveys, or analyze customer support interactions to gauge customer satisfaction and sentiment regarding personalized experiences driven by the CDP. Positive customer feedback and higher satisfaction scores indicate successful implementation and positive customer experiences.
It's important for businesses to define their specific success metrics and KPIs based on their unique goals and objectives. Regular monitoring, analysis, and optimization based on these metrics can help businesses assess the success of their CDP implementation and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.




